Law students at College of Law of YU must successfully complete 131 Credit Hours through 41 compulsory legal courses, as well as 4 elective courses.
The study plan of the College of Law is one of the most innovative higher educational programs in the country designed by senior experienced academics and higher education professionals to allow law students to progressively advance smoothly and practically in their legal studies in a manner that is intended to build upon previously completed law courses and accumulated Credit Hours.
As such, each semester, students are expected to finish certain major law courses as requirements/pre-requisites to register in new law course in the following semester. Some courses may also require that students accumulate a particular number of credit hours before they are able to register in them.
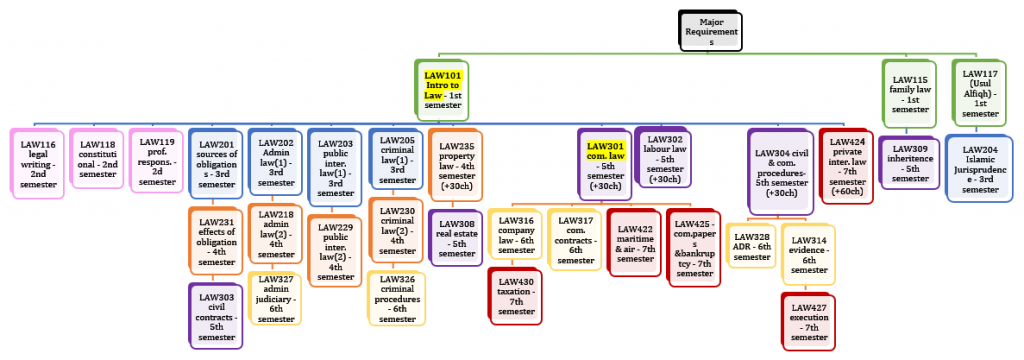
The process takes place over a course of 4 levels consisting of 8 academic semesters as explained in the College’s study plan. The following chart illustrates the major law courses requirements that the students must complete to be able to advance through their study plan hierarchically:

Course Pre-requisites:
As demonstrated from the above chart, the following courses are considered major requirements for any law student who wishes to advance in his/her study plan by efficiently moving from one level to the next:
- LAW101 (introduction to law – 1st semester) opens 12 compulsory law courses to students who successfully complete it throughout the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 7th
- During the 3rd semester, students who successfully complete LAW201 (sources of obligations), LAW202 (administrative law-1), LAW203 (public international law-1), & LAW205 (criminal law-1) will be able to register in almost all the 4th semester’s courses (excepted for LAW235 property law which requires that students must have successfully completed LAW101 + 30 Credit Hours).
- LAW301 (commercial Law – 5th semester) opens 4 compulsory law courses to students who successfully complete it throughout the 6th & 7th
- LAW304 (civil & commercial procedures – 5th semester) is another major requirement that allows students, if successfully completed, to register in two compulsory law courses on the 6th
Credit Hours Pre-requisites:
It is also important to realise that merely completing a particular course’s pre-requisite will not always open other courses for students. Many pre-requisites require that students have also managed to accumulate a particular number of Credit Hours beside the successful completion of a pre-requisite course. For Instance:
- While LAW101 opens 12 other courses for students, 5 of these courses will require students to have completed a particular number of Credit hours beside completing the pre-requisite course:
- LAW235 (property law – 4th semester) requires students to have completed 30 CH + successfully completing LAW101.
- LAW301 (commercial law – 5th semester) requires students to have completed 30 CH + successfully completing LAW101.
- LAW302 (labour law – 5th semester) requires students to have completed 30 CH + successfully completing LAW101.
- LAW304 (civil & commercial procedures – 5th semester) requires students to have completed 30 CH + successfully completing LAW101.
- LAW425 (private international law – 7th semester) requires students to have completed 60 CH + successfully completing LAW101.
- A few law courses on the law study plan will not have a pre-requisite course but will rather require students to merely have completed a particular number of Credit Hours. For instance:
- LAW429 (Intellectual Property – 7th semester) will require students to have completed at least 70 CH before they are able to register in that course.
- LAW411 (training & research) will require students to have completed at least 90 CH before they are able to begin their Co-Op training.
- All elective law courses require students to have at least completed 30 CH before they can register in any of these courses.
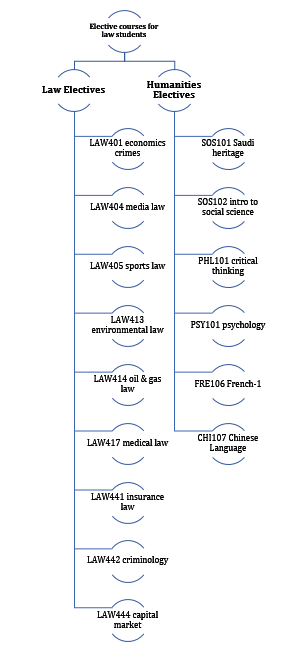
Elective Courses:
Finally, it is important to note that study plan of the College of Law provides for two types of elective courses. These are Law, as well as Humanities & Social Science elective courses. Each type has its own requirements before registration and, as such, students must pay attention to the specific requirements of each category.